1. 서론
근육세포는 미분화 상태의 근아세포(myoblast)에서 근관세포(myotube)로 근분화(myogenesis) 과정을 통해 분화된다(Bentzinger 등, 2012; Burattini 등, 2009). 근육세포 분화는 MyoD, myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs), MHC 등과 같은 조절인자의 발현량이 증가하며 조절되는 것으로 알려져 있으며, 이러한 조절 인자들은 근육세포 분화의 표지 인자로 사용되고 있다(Bentzinger 등, 2012; Ferri 등, 2009; Hasty 등, 1993; Jeong 등, 2011). 근육량의 감소는 30대부터 진행되어 40대 이후부터 10년마다 8%, 70대 이후에는 10년마다 최대 15%씩 감소할 수 있다(Jung 등, 2016). 근육량 감소는 호르몬 불균형이나 영양 결핍, 만성적인 체내 염증에 의해서도 생기지만 가장 주된 원인은 노화로 알려져 있으며, 최근 고령 인구가 급속하게 증가함에 따라 근육량이 감소하면서 발생하는 근감소증 유병률은 지속적으로 증가하고 있다(Rhee, 2013). 이는 신체 기능 저하를 일으키며, 삶의 질 저하뿐만 아니라 낙상이나 골절 및 당뇨병과 심혈관질환 등 치명적인 만성 질환들의 발생 위험도를 증가 시킴으로써 이로 인해 지출되는 사회적 비용과 사망률을 증가시키는 원인으로 알려져 있다(Choi 등, 2020a; Dao 등, 2021; Hong과 Choi, 2012; Kwak과 Kim, 2007; Rhee, 2013).
과격한 운동, 노화 등에 의해 비정상적으로 증가된 reactive oxygen species (ROS)는 산화적 스트레스를 유발하며 단백질의 산화와 손상, 미토콘드리아의 기능 장애, 여러 세포 내 신호전달 체계를 활성화시킨다(Cho 등, 2008; Stangel 등, 1996). 산화적 스트레스는 세포의 노화와 사멸을 유도하여 근육세포의 손상을 일으키고 근육세포의 기능 저하와 연관되어 있다고 보고되고 있으며 근감소증의 발생에 주된 인자로 여겨지고 있다(Brioche와 Lemoine-Morel, 2016).
오랜 기간 치료에 사용되며 얻은 결과들을 바탕으로 검증된 생리 활성과 낮은 부작용으로 인해 천연물로부터 질병 예방 및 치료에 효과를 가지는 기능성 소재를 개발하기 위한 연구들이 진행되고 있다. 근육세포의 분화와 증식, 산화적 스트레스에 의한 손상 방어 효과를 나타낼 수 있는 부작용과 독성이 낮은 천연물을 이용한 연구가 꾸준히 이루어지고 있다 (Chae와 Nam, 2020; Cho 등, 2017; Mason과 Wadley, 2014; Park 등, 2019). 최근에는 단일 천연물을 이용한 소재 개발 연구에서 여러 종류의 천연물 배합을 통해 시너지 효과가 동반되어 생리활성 효과를 극대화시킬 수 있도록 연구가 진행되고 있다(Choi 등, 2017; Yoon 등, 2013). 여러 종류가 배합된 천연물은 다양한 성분들을 함유하고 있어 광범위하게 적용 가능하며, 천연물의 추출 방법이나 배합 비율에 따라서 효과가 달라지므로 다양한 복합 소재 개발이 가능하다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 다양한 천연물을 활용한 복합 소재의 새로운 효능을 확인하기 위해 항산화, 근육세포 분화, 근위축 억제, 근육 노화 억제, 세포 보호 효과가 있는 것으로 확인된 상엽, 산수유, 도라지, 진피, 꾸지뽕, 구기자, 생강 및 유자로 구성된 식물 추출물 혼합 분말의 C2C12 근육세포 분화 및 H2O2에 의한 산화적 스트레스에 대한 세포 보호 효과를 검증하여 식물 복합 추출물이 근감소 억제에 도움을 줄 수 있는 기능성 소재로써 개발에 필요한 자료를 제공하려고 한다(Cho, 2017; Choi와 Kim, 2022; Jang, 2022; Jeong과 Shim, 2006; Kim 등, 2020; Lee 등, 2015; Lee 등, 2021; Lee 등, 2018; Ma 등, 2019; Yoo 등, 2005).
2. 재료 및 방법
Fetal bovine serum (FBS, #S001-01)은 Welgene (Gyeongsan, Korea)에서 구매하여 사용하였다. Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM, #11995065), horse serum (HS, #16050122), phosphate buffered saline (PBS, #14190144), bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay kit (#23225), enhanced chemiluminescent substrate (#34577)는 Thermo fisher (Waltham, MA, USA)에서 구매하여 사용하였다. 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT, #M5655), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, #D8418), radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer (#R0278), H2O2 (#216743)는 Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA)에서 구입하여 사용하였다. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane (#03010040001), cytotoxicity detection kit (#11644793001)는 Roche Diagnostics (Mannheim, Germany)에서 구입하여 사용하였다. Creatine kinase activity assay kit (#ab155901)는 abcam (Cambridge, UK)에서 구입하여 사용하였다. 10% mini-protean TGXTM precast protein gel (#4561033), everyblot blocking buffer (#12010020)는 Bio-rad (Hercules, CA, USA)에서 구입하여 사용하였다. 또한, western blot에 사용된 myosin heavy chain (MHC), myogenin, cleaved caspase-3 (#9664), cleaved caspase-9 (#9509), Bcl-2 (#3498), Bax (#sc-70405), β-actin (#3700) 및 Anti-rabbit IgG (#7074), Anti-mouse IgG (#7076)는 Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA) 및 Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA, USA)에서 구입하여 사용하였다.
상엽, 산수유, 도라지, 진피, 꾸지뽕, 구기자, 생강 및 유자는 동부생약 영농조합법인(북위 34°92'59."N, 경도 127°52'28."E)에서 2021년 구입하여 다음과 같은 방법으로 동일하게 추출하여 농축하고 이를 분말화하여 시료로 사용하였다. 즉, 각각의 원재료를 2-3 cm 사이로 세절한 뒤 300 g에 증류수 300 mL을 가하고 6-7시간 동안 85-90°C로 상압 조건에서 가열하여 원재료별로 각각의 추출액을 제조하였다. 여과지(Advantec, Tokyo, Japan)를 이용하여 추출액들을 여과하였으며, 감압농축기(N-1000, Tokyo Rikakikai, Tokyo, Japan)로 고형분이 20-25 wt%가 되도록 농축하고 동결건조기(MP-9005, Marueda, Gwangju, Korea)를 이용하여 시료별로 분말화하였다. 분말 상태의 각각의 추출물들은 상엽 25%, 산수유 16.8%, 도라지 16.7%, 진피 8.3%, 꾸지뽕 8.3%, 구기자 8.3%, 생강 8.3% 및 유자 8.3%의 비율로 혼합하여 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 만든 후 실험에 사용하였다.
본 연구에 사용된 마우스 유래 C2C12 근육세포는 American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA)으로부터 분양받아 사용하였으며, 10% FBS와 1% antibiotic-antimycotic이 함유된 DMEM 배지를 사용하여 5% CO2, 37°C로 조절된 배양기를 이용하여 배양하며 실험에 사용하였다. C2C12 근육세포의 분화 유도를 위해 2% HS를 함유한 DMEM 배지로 교체하였으며, 2일마다 배지 교체 및 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 처리하고 6일 동안 분화를 유도하였다.
C2C12 근육세포를 96 well plate에 1×104 cells/well로 각 well에 분주하였다. 24시간 동안 배양한 후, 식물 추출물 혼합 분말은 0, 50, 100, 500, 700, 900, 1,000 μg/mL, H2O2은 0, 50, 100, 300, 500, 700 μM로 DMEM을 이용하여 희석한 후 처리하고 24시간 동안 배양하였다. 그 후, 배지를 모두 제거하고 DMEM 배지로 MTT를 0.5 μg/mL 농도로 희석하여 각 well에 100 μL씩 처리하고 4시간 동안 배양하였다. 배지를 완전히 제거하고 각 well에 DMSO 100 μL씩 처리하였다. 세포에 형성된 formazan을 용출시키기 위해 실온에서 10분간 반응시킨 후 versamax microplate reader (Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA)를 이용하여 540 nm에서 흡광도를 측정하였다. 세포 보호 효과를 확인하기 위해 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 300, 400, 500 μg/mL로 4시간 처리한 후 500 μM H2O2를 24시간 동안 처리하여 산화적 스트레스를 유발하였다. 그 후 MTT assay 과정은 세포 독성 평가와 동일한 과정으로 진행하여 세포 보호 효과를 확인하였다.
C2C12 근육세포에 세포 보호 효과 평가와 동일한 조건으로 식물 추출물 혼합 분말과 H2O2 처리가 완료된 후 수집한 배지 내 LDH 활성은 cytotoxicity detection kit를 이용하여 kit에서 제공한 실험방법에 따라 측정하였다.
C2C12 근육세포에 세포 보호 효과 평가와 동일한 조건으로 추출물과 H2O2 처리가 완료된 후 배지를 제거하고 세포를 모아 lysis buffer (PBS containing 0.1% Tween-20)를 처리하였다. 4°C, 12,000 rpm으로 15분 동안 원심분리를 하여 얻은 상층액을 CK 활성 측정에 이용하였다. CK 활성은 creatine kinase activity assay kit를 이용하여 kit에서 제공하는 실험방법에 따라 진행하여 측정하였다.
처리가 완료된 C2C12 근육세포를 PBS로 세척하고, 세포를 모아 RIPA buffer를 20분간 4°C에서 처리하였다. 4°C, 12,000 rpm으로 20분간 원심분리하고 BCA protein assay kit를 이용하여 상층액 내 단백질 농도를 정량하였다. 동량의 단백질을 10% mini-protean TGXTM precast protein gel을 이용하여 전기영동한 후 PVDF membrane에 전이시켰다. Everyblot blocking buffer로 상온에서 10분 동안 membrane을 blocking하고, primary antibody (1:1,000-1:5,000)를 4°C에서 하룻밤 동안 반응시킨 후, 1X tris-buffered saline with 0.1% Tween-20 (TBS-T)으로 PVDF membrane을 15분씩 3회 세척하였다. 희석된 HRP-conjugated secondary antibody (1:1,000-1:4,000)를 상온에서 2-3시간 반응시킨 후, 1X TBS-T를 이용하여 PVDF membrane을 15분씩 3회 세척하였다. 이후, enhanced chemiluminescent substrate를 처리하고 Microchemi 4.2 (DNR, Neve Yamin, IS)로 PVDF membrane에 나타난 protein band를 관찰하여 발현 정도를 분석하였다.
3. 결과 및 고찰
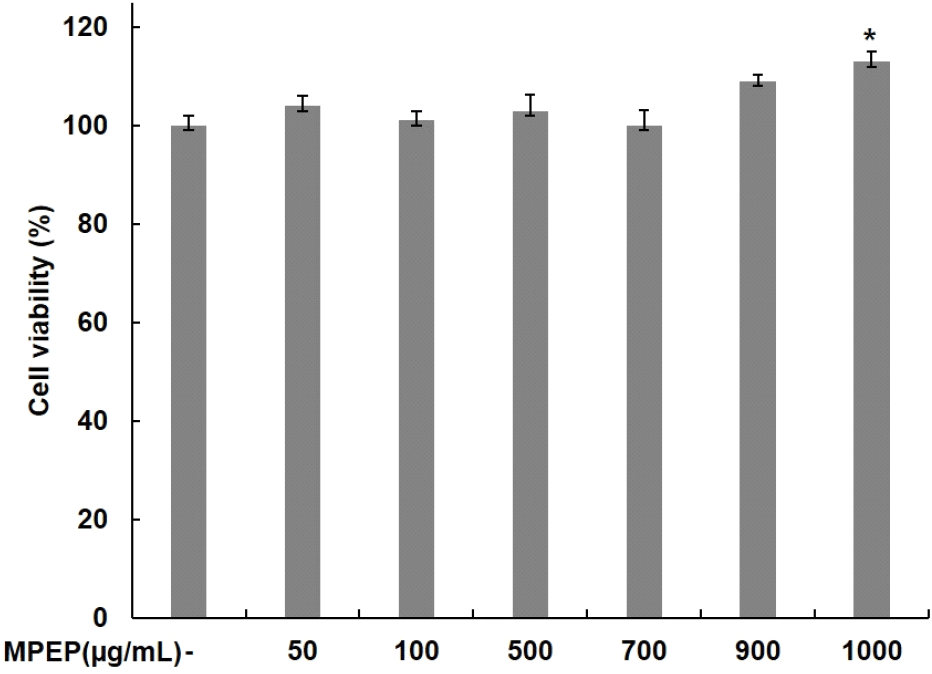
C2C12 근육세포에 대한 식물 추출물 혼합 분말의 세포독성을 확인하기 위해 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 농도별로 24시간 동안 처리하고 MTT assay를 통해 세포독성을 평가하였다. 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 0, 50, 100, 500, 700, 900, 1,000 μg/mL의 농도로 24시간 동안 처리한 결과, Fig. 1에서 보여주는 바와 같이 농도별로 104, 101, 103, 100, 109, 113%의 생존율을 나타냈으며, 1,000 μg/mL까지 세포독성이 나타나지 않았다. 세포독성을 나타내지 않은 농도 이하로 처리하여 다음 실험을 진행하였다.
분화과정 동안 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 300, 400, 500 μg/mL 농도로 처리하고, 분화 유도 인자인 myogenin과 MHC의 발현 변화를 확인하여, 식물 추출물 혼합 분말의 근육세포 분화에 대한 효과 여부를 western blot을 이용하여 확인하였다. MHC의 경우, 무처리군에 비해 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 처리한 군은 300 μg/mL는 67%, 400 μg/mL는 89%, 500 μg/mL는 62% 증가하였고(Fig. 2A), myogenin의 경우, 무처리군에 비해 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 처리한 군 중 300 μg/mL는 137%, 400 μg/mL는 156%, 500 μg/mL는 248% 증가하였다(Fig. 2B).
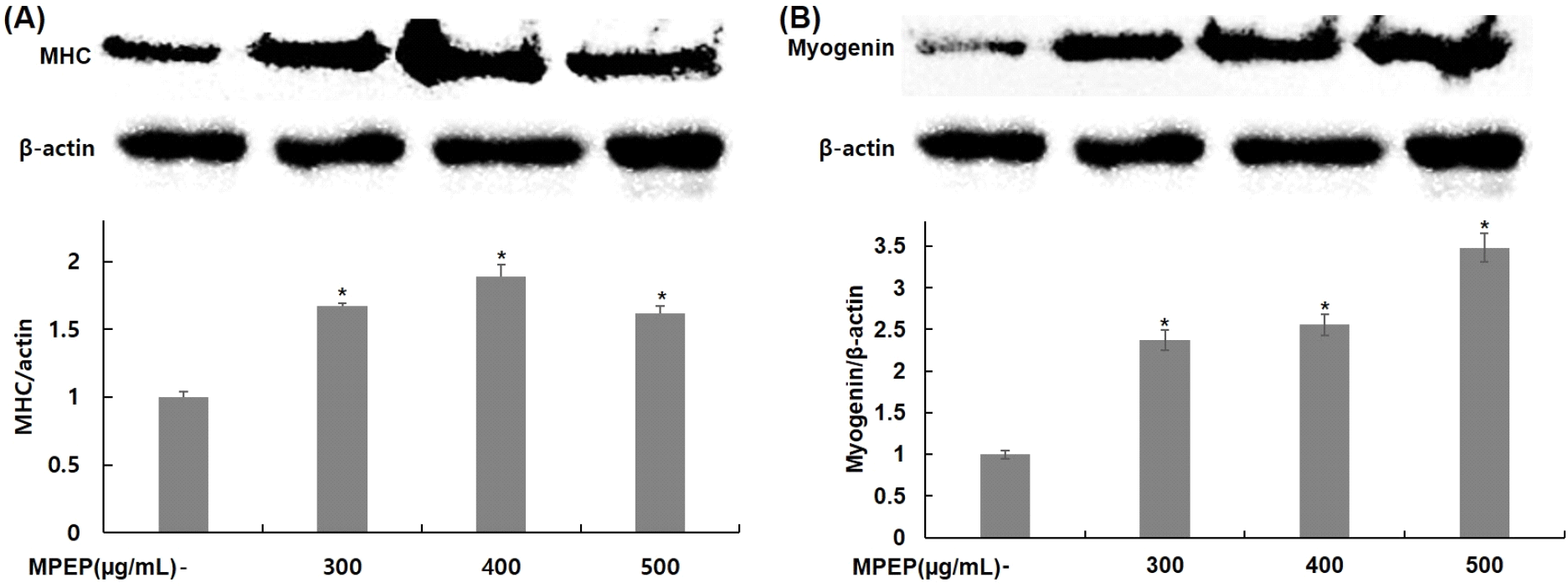
근육세포의 분화는 다양한 분화 유도 인자들에 의해 조절된다. 분화 초기에 발현이 증가하는 MyoD는 세포 주기를 조절하여 증식을 억제하고 분화를 촉진하고, myogenin의 upstream에 위치하며 분화과정을 조절한다(Hasty 등, 1993). 분화 후기에 myogenin은 근관의 형성을 유도하고 세포 중기를 중지시키며, 미오신 구성 단백질 중 하나인 MHC와 같은 유도 인자들과 함께 발현이 증가한다(Bentzinger 등, 2012; Ferri 등, 2009). Kang 등(2019)의 연구에서는 모과추출물에 의해 myogenin과 MHC의 발현이 증가하고, 근관의 형성이 이루어지는 것으로 나타났으며, 이를 통해서 분화 촉진에 도움을 주는 것을 확인하였다. 또한, Song (2015)은 백출 추출물에 의해 MyoD, Mrf 5, MHC의 발현 증가를 통해 근육 분화를 유도한다고 보고하였다. 본 연구에서도 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 처리한 군의 myogenin과 MHC의 발현이 증가함을 확인하였으며, 이를 통해서 식물 추출물 혼합 분말이 근육세포의 분화 유도 효과가 있는 것으로 판단된다.
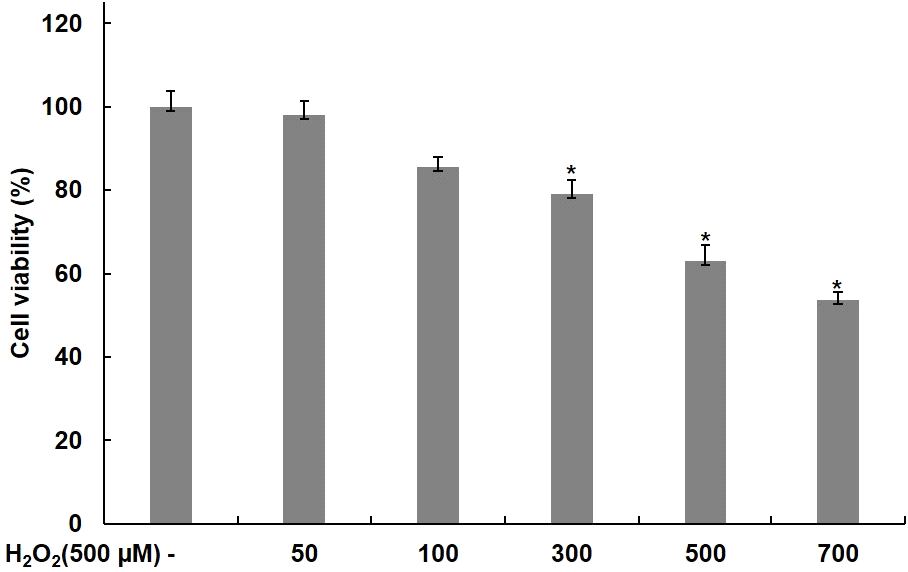
C2C12 근육세포에 대한 H2O2의 세포독성을 확인하기 위해 H2O2를 농도별로 24시간 동안 처리하고, MTT assay를 통해 세포독성을 평가하였다. H2O2를 0, 50, 100, 300, 500, 700 μM의 농도로 24시간 동안 처리한 결과, Fig. 3에서 보여주는 바와 같이 농도별로 98, 85, 79, 63, 53%의 생존율을 나타냈다. 따라서 산화적 스트레스에 대한 세포 보호 효과를 확인하기 위한 H2O2 처리농도는 500 μM로 설정하였다.
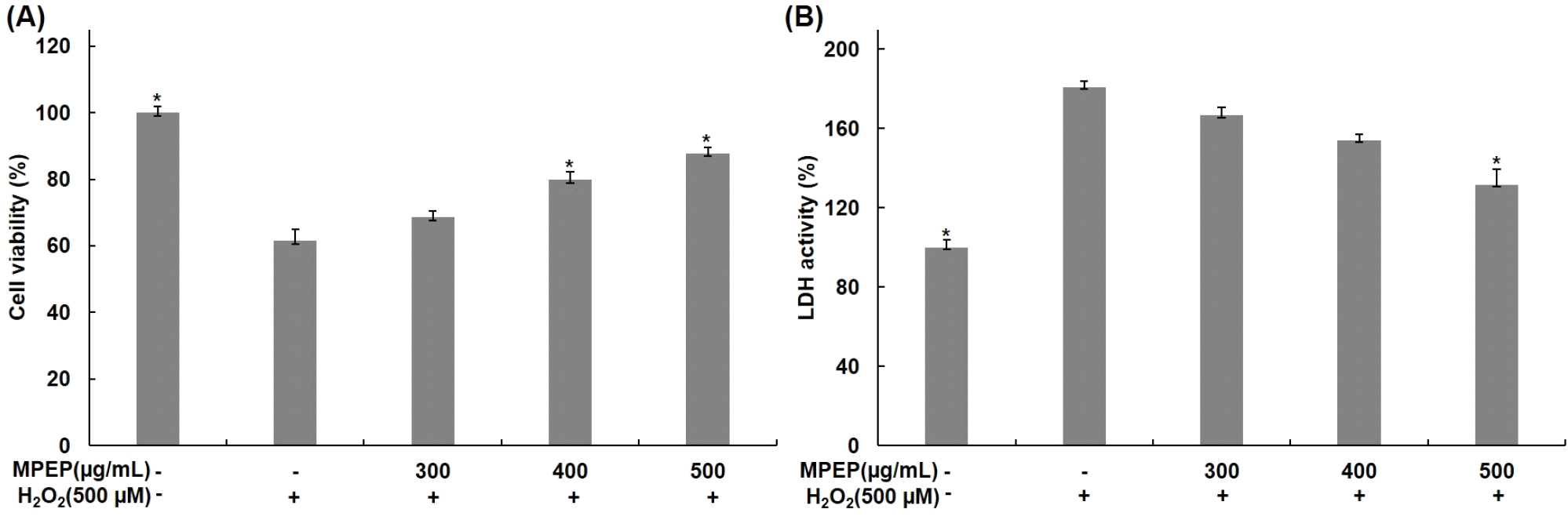
H2O2에 대한 세포 보호 효과를 확인하기 위해 분화된 C2C12 근육세포에 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 300, 400, 500 μg/mL 농도로 4시간 전처리한 후 배지에 500 μM H2O2를 24시간 동안 처리하고, MTT assay와 LDH assay를 통해 확인하였다. MTT assay를 통해 확인한 결과, 무처리군에 비해 H2O2 단독 처리 군에서는 세포 생존율이 61%로 감소하였지만, 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 처리한 군에서는 68, 79, 87%로 세포 생존율이 증가하였으며, H2O2 단독 처리 군과 비교했을 때 세포 생존율이 각각 11, 29, 42% 증가함을 확인하였다(Fig. 4A). 또한, LDH assay를 통해 확인한 결과에서도 무처리군에 비해 H2O2 단독 처리 군에서는 LDH 활성이 180%로 증가하였지만, 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 처리한 군에서는 166, 154, 131%로 LDH 활성이 감소하였으며, H2O2 단독 처리 군과 비교했을 때 LDH 활성이 각각 8, 15, 27% 감소함을 확인하였다(Fig. 4B). H2O2에 의한 산화적 스트레스와 같은 외부 자극에 의해 세포막 손상과 함께 세포 사멸이 발생하면 LDH 방출이 증가하여 LDH는 세포 사멸의 지표로 이용된다(Choi 등, 2020b). Seong 등(2022)의 연구에서도 H2O2를 처리하여 산화적 스트레스를 유도한 C2C12 근육세포에서 세포 사멸이 증가함을 확인하였으며, 천심련 추출물 처리에 의한 세포 생존율 증가 및 LDH 감소를 통해 천심련 추출물이 산화적 스트레스에 대한 세포 보호 효과를 가지고 있으며, 근손상 억제 효과를 나타내는 것으로 보고하였다. 식물 추출물 혼합 분말 처리에 의해 세포 생존율 증가 및 LDH 감소를 확인하였으며, 이를 통해 식물 추출물 혼합 분말이 H2O2에 의한 산화적 스트레스에 의한 세포 사멸을 억제하고, 근육세포 보호 효과를 가지고 있는 것으로 판단된다.
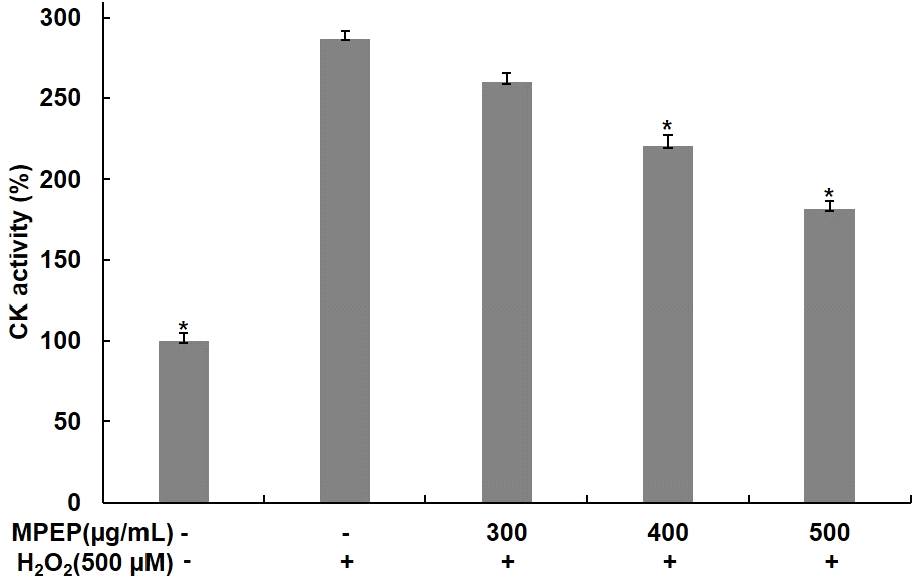
CK는 creatine을 phoaphocreatine과 ADP로 전화시켜 근육이 수축하는 동안 에너지 대사를 조절하는 역할을 한다(Perry 등, 2008). 본 연구에서는 분화된 C2C12 근육세포에 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 300, 400, 500 μg/mL 농도로 4시간 전처리한 후 배지에 500 μM H2O2를 24시간 동안 처리하고, CK의 활성을 측정하여 산화적 스트레스에 의해 증가된 CK 활성에 식물 추출물 혼합 분말이 미치는 영향을 확인하였다. 무처리군에 비해 H2O2만 단독으로 처리한 군에서는 CK 생성이 286%로 증가하였지만, 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 처리한 군에서는 259, 220, 181%로 CK 활성이 감소하였으며, H2O2 단독 처리 군과 비교했을 때 CK 활성이 각각 9, 23, 36% 감소함을 확인하였다(Fig. 5). 산화적 스트레스는 phosphocreatine system을 통해 CK의 활성화와 혈중 내 방출을 증가시켜 근육 손상과 피로 정도를 나타내는 지표로 여겨진다(Seong 등, 2022; Ydfors 등, 2016). Buyanbadrakh 등(2020)의 연구에서도 H2O2를 처리하여 산화적 스트레스를 유도한 C2C12 세포에서 마카 추출물 처리에 의해 CK 활성이 감소를 확인하였고, 이를 통해서 마카 추출물이 산화적 스트레스에 대한 보호 효과가 있음을 보고하였다. 따라서 본 연구 결과는 식물 추출물 혼합 분말이 산화적 스트레스로부터 근육세포 보호뿐만 아니라, 근육 피로 감소 효과를 가지고 있음을 나타내는 것으로 판단된다.
본 연구에서는 분화된 C2C12 근육세포에서 산화적 스트레스에 대한 식물 복합 추출물의 세포 보호 효과가 apoptosis 경로 억제 여부에 의한 것인지 확인하기 위해 분화된 C2C12 근육세포에 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 300, 400, 500 μg/mL 농도로 4시간 전처리한 후 배지에 500 μM H2O2를 24시간 동안 처리하고 western blot을 이용하여 관련 단백질 발현 정도를 확인하였다(Fig. 6). 먼저 H2O2에 의한 apoptosis 억제 효과가 Bcl-2 family와 연관되어 있는지를 확인하기 위해 Bax와 Bcl-2 발현 변화를 확인하였다. 무처리군에 비해 H2O2 단독 처리군은 Bax의 발현 증가와 Bcl-2의 발현이 감소함을 확인하였다. 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 처리한 군은 H2O2 단독 처리 군보다 Bax는 18, 17, 41% 발현이 감소하였고(Fig. 6A), Bcl-2는 200, 1,325, 2,125% 발현이 증가하였다(Fig. 6B). 또한, H2O2에 의한 apoptosis의 핵심조절인자로 작용하는 효소인 caspase의 차단에 의한 것인지를 확인하기 위해 caspase-9과 -3 발현 변화를 확인하였다. 무처리군에 비해 H2O2 단독 처리군은 caspase-9과 -3의 발현이 증가함을 확인하였지만, 식물 추출물 혼합 분말을 처리한 군은 H2O2 단독으로 처리한 군보다 caspase-9는 2, 26, 43% 발현이 감소하였고(Fig. 6C), caspase-3는 15, 36, 60% 발현이 감소하였다(Fig. 6D). 이러한 결과는 식물 추출물 혼합 분말의 apoptosis 억제 효과는 Bcl-2 family 단백질 발현 조절과 caspase 활성 억제와 연관되어 있으며 이로 인해 식물 추출물 혼합 분말의 세포 보호 효과를 나타냄을 알 수 있었다.
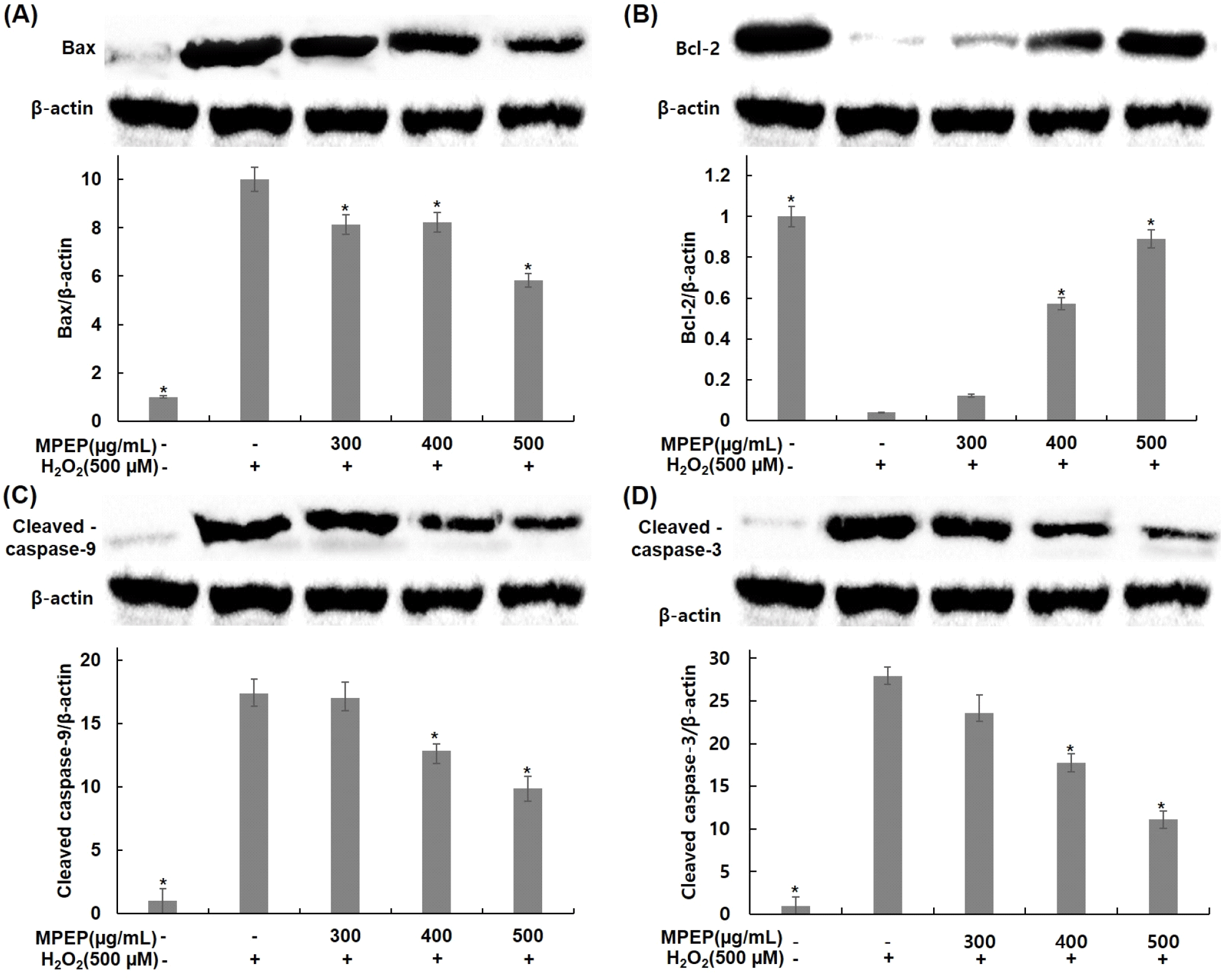
Intrinsic apoptosis 경로에서 Bcl-2 family protein들은 anti-apoptotic과 pro-apoptotic protein으로서 역할을 하며, 그들 간의 상호작용은 apoptosis 경로에서 중요한 요소로 작용한다(Leibowitz과 Yu, 2010). H2O2는 ROS의 생성을 증가시킴으로써 산화적 스트레스를 유발하여 intrinsic apoptosis 경로에 관여하는 Bcl-2 family의 발현 수준을 조절하는 것으로 알려져 있다(Susnow 등, 2009). 이는 Bax의 활성화 및 Bcl-2 발현을 억제를 통해 하위경로인 caspase에 의한 apoptosis 경로를 활성화하는 전형적인 과정인 apoptosome 형성에 관여하며, 형성된 apoptosome에 의해 활성화된 caspase-9은 caspase-3를 포함한 caspase family의 활성화를 증가시키고, 최종적으로 apoptosis를 유발한다(Tsujimoto, 1998). 본 연구에서도 H2O2에 의해 Bax의 발현 증가 및 Bcl-2 발현 억제, caspase-9와 -3 활성화 증가를 확인하였으며, 식물 추출물 혼합 분말 처리에 의해 Bax의 발현 감소 및 Bcl-2 발현 증가뿐만 아니라, caspase-9, -3의 활성화 또한 감소함을 확인하였다. 이러한 결과들을 통해서 H2O2로 유발된 산화적 스트레스에 의한 apoptosis 감소는 식물 추출물 혼합 분말의 Bcl-2 family protein의 발현 조절에 의한 caspase의 활성 억제에 따른 결과임을 확인할 수 있었으며, 이는 식물 추출물 혼합 분말이 산화적 스트레스에 대한 근육세포 보호 효과를 가지고 있음을 보여주는 결과이다. Choi(2015)의 연구에서도 H2O2를 처리하여 산화적 스트레스를 유발한 C2C12 근육세포에서 apoptosis 관련 Bcl-2 family protein 및 capase-9, -3의 발현과 활성화에 미치는 영향을 확인한 결과, isorhamnetin 처리에 의한 Bax의 발현 감소 및 Bcl-2의 발현 증가, capase-9, -3의 활성화 감소를 통해 intrinsic apoptosis 경로를 억제함으로써 산화적 스트레스에 의한 apoptosis로부터 세포 보호 효과가 있음을 보여주고 있다.
본 연구를 통해서 식물 추출물 혼합 분말이 myogenin, MHC의 발현 증가를 통해 근육세포의 분화 유도 효과와 Bcl-2 family에 포함되는 Bax와 Bcl-2의 발현 조절, caspase-9와 -3 활성화 억제에 의한 intrinsic apoptosis 경로 억제를 통해 apoptosis을 감소시켜 H2O2에 의해 유도된 산화적 스트레스로부터 세포 보호 효과가 있음을 확인하였다. 따라서 식물 추출물 혼합 분말이 근육세포 분화 및 산화적 스트레스에 대한 세포 보호 효과를 나타냄으로써 근감소증 개선을 위한 기능성 소재로서의 가능성이 있는 것으로 판단된다.
4. 요약
본 연구에서는 식물 추출물 혼합 분말의 근육세포 분화 및 산화적 스트레스에 대한 세포 보호 효과를 확인하고자 하였다. 추출물을 최대 1,000 μg/mL 농도까지 세포에 처리한 결과, 세포 생존율이 감소하지 않음을 확인되었다. 식물 추출물 혼합 분말이 근육세포 분화 인자에 미치는 영향을 확인하기 위해 myogenin과 MHC의 발현 여부를 확인한 결과, 무처리군에 비해 발현이 증가함을 확인하였다. H2O2에 의해 유도된 산화적 스트레스에 대한 세포 보호 효과를 확인한 결과, 식물 추출물 혼합 분말 처리에 의해 H2O2 단독 처리군보다 세포 생존율이 증가하였으며, LDH와 creatine kinase의 활성이 감소하였다. 또한, Bax와 Bcl-2의 발현을 조절하여 caspase-9와 -3 활성화를 억제함을 확인하였다. 이를 통해 식물 추출물 혼합 분말의 근육세포 분화 효과 및 H2O2에 의해 유도된 산화적 스트레스에 대한 세포 보호 효과가 있음을 확인하였다. 따라서 식물 추출물 혼합 분말은 근감소증 개선을 위한 기능성 소재로써 활용이 가능할 것으로 판단되며, 향후 근감소증 개선을 위한 기능성 소재로서의 유효성 확보를 위해서 근감소증 세포 및 동물모델을 이용한 효능 및 기전 분석 연구가 더 필요할 것으로 사료된다.











